Hierarchical Dependency Injectors 6.0
You learned the basics of Angular Dependency injection in the Dependency Injection page. Angular has a Hierarchical Dependency Injection system: there is actually a tree of injectors that parallel an app’s component tree. You can reconfigure the injectors at any level of that component tree.
In this page you’ll explore this system and learn how to use it to your advantage. Try the live example (view source).
The injector tree
In the Dependency Injection page, you learned how to configure a dependency injector and how to retrieve dependencies where you need them.
In fact, there is no such thing as the injector. An app may have multiple injectors. An Angular app is a tree of components. Each component instance has its own injector. The tree of injectors parallels the tree of components.
A component’s injector may be a proxy for an ancestor injector higher in the component tree. That’s an implementation detail that improves efficiency. You won’t notice the difference and your mental model should be that every component has its own injector.
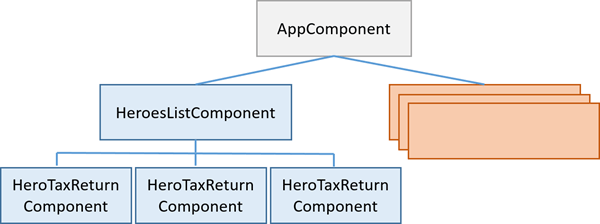
Consider this guide’s variation on the Tour of Heroes app.
At the top is the AppComponent which has some subcomponents.
One of them is the HeroesListComponent.
The HeroesListComponent holds and manages multiple instances of the HeroTaxReturnComponent.
The following diagram illustrates a three-level component tree when there are three instances of HeroTaxReturnComponent
open simultaneously.
Injector bubbling
When a component requests a dependency, Angular tries to satisfy that dependency with a provider registered in that component’s own injector. If the component’s injector lacks the provider, it passes the request up to its parent component’s injector. If that injector can’t satisfy the request, it passes it along to its parent injector. The requests keep bubbling up until Angular finds an injector that can handle the request or runs out of injectors. If it runs out of injectors, Angular throws an error.
You can cap the bubbling. An intermediate component can declare that it is the “host” component. The hunt for providers will climb no higher than the injector for that host component. This is a topic for another day.
Re-providing a service at different levels
You can re-register a provider for a particular dependency token at multiple levels of the injector tree, but you shouldn’t do so unless you have a good reason.
Since the lookup logic works upwards, the first provider encountered wins. Thus, a provider in an intermediate injector intercepts a request for a service from something lower in the tree. It effectively shadows a provider at a higher level in the tree.
If you only specify providers at the top level (typically the root AppComponent), the tree of injectors appears to be flat.
All requests bubble up to the root injector that you configured with the runApp() method.
Component injectors
The ability to configure one or more providers at different levels opens up interesting and useful possibilities.
Scenario: service isolation
Architectural reasons may lead you to restrict access to a service to the app domain where it belongs.
The sample app includes a VillainsListComponent that displays a list of villains.
It gets those villains from a VillainsService.
While you could provide VillainsService in the root AppComponent (that’s where you’ll find the HeroesService),
that would make the VillainsService available everywhere in the app, including the Hero workflows.
If you later modified the VillainsService, you could break something in a hero component somewhere.
That’s not supposed to happen but providing the service in AppComponent creates that risk.
Instead, provide the VillainsService in the providers metadata of the VillainsListComponent like this:
lib/src/villains_list_component.dart (metadata)
@Component(
selector: 'villains-list',
template: '''
<div>
<h3>Villains</h3>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let villain of villains | async">{{villain.name}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
''',
directives: [coreDirectives],
providers: [ClassProvider(VillainsService)],
pipes: [commonPipes],
)By providing VillainsService in the VillainsListComponent metadata and nowhere else,
the service becomes available only in the VillainsListComponent and its subcomponent tree.
It’s still a singleton, but it’s a singleton that exist solely in the villain domain.
Now you know that a hero component can’t access it. You’ve reduced your exposure to error.
Scenario: multiple edit sessions
Many apps allow users to work on several open tasks at the same time. For example, in a tax preparation app, the preparer could be working on several tax returns, switching from one to the other throughout the day.
The sample app demonstrates that scenario with an example in the Tour of Heroes theme.
Imagine an outer HeroListComponent that displays a list of heroes.
To open a hero’s tax return, the preparer clicks on a hero name, which opens a component for editing that return. Each selected hero tax return opens in its own component and multiple returns can be open at the same time.
Each tax return component has the following characteristics:
- Is its own tax return editing session.
- Can change a tax return without affecting a return in another component.
- Has the ability to save the changes to its tax return or cancel them.

One might suppose that the HeroTaxReturnComponent has logic to manage and restore changes.
That would be a pretty easy task for a simple hero tax return.
In the real world, with a rich tax return data model, the change management would be tricky.
You might delegate that management to a helper service, as this example does.
Here is the HeroTaxReturnService.
It caches a single HeroTaxReturn, tracks changes to that return, and can save or restore it.
It also delegates to the app-wide singleton HeroService, which it gets by injection.
lib/src/hero_tax_return_service.dart
import 'dart:async';
import 'hero.dart';
import 'heroes_service.dart';
class HeroTaxReturnService {
final HeroesService _heroService;
HeroTaxReturn _currentTR, _originalTR;
HeroTaxReturnService(this._heroService);
void set taxReturn(HeroTaxReturn htr) {
_originalTR = htr;
_currentTR = HeroTaxReturn.copy(htr);
}
HeroTaxReturn get taxReturn => _currentTR;
void restoreTaxReturn() {
taxReturn = _originalTR;
}
Future<void> saveTaxReturn() async {
taxReturn = _currentTR;
await _heroService.saveTaxReturn(_currentTR);
}
}Here is the HeroTaxReturnComponent that makes use of it.
lib/src/hero_tax_return_component.dart
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:angular/angular.dart';
import 'package:angular_forms/angular_forms.dart';
import 'hero.dart';
import 'hero_tax_return_service.dart';
@Component(
selector: 'hero-tax-return',
template: '''
<div class="tax-return">
<div class="msg" [class.canceled]="message==='Canceled'">{{message}}</div>
<fieldset>
<span id="name">{{taxReturn.name}}</span>
<label id="tid">TID: {{taxReturn.taxId}}</label>
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<label>
Income: <input type="number" [(ngModel)]="taxReturn.income" class="num">
</label>
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<label>Tax: {{taxReturn.tax}}</label>
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<button (click)="onSaved()">Save</button>
<button (click)="onCanceled()">Cancel</button>
<button (click)="onClose()">Close</button>
</fieldset>
</div>
''',
styleUrls: ['hero_tax_return_component.css'],
directives: [coreDirectives, formDirectives],
providers: [ClassProvider(HeroTaxReturnService)],
)
class HeroTaxReturnComponent {
final HeroTaxReturnService _heroTaxReturnService;
String message = '';
HeroTaxReturnComponent(this._heroTaxReturnService);
final _close = StreamController<Null>();
@Output()
Stream<Null> get close => _close.stream;
HeroTaxReturn get taxReturn => _heroTaxReturnService.taxReturn;
@Input()
void set taxReturn(HeroTaxReturn htr) {
_heroTaxReturnService.taxReturn = htr;
}
Future<void> onCanceled() async {
_heroTaxReturnService.restoreTaxReturn();
await flashMessage('Canceled');
}
void onClose() => _close.add(null);
Future<void> onSaved() async {
await _heroTaxReturnService.saveTaxReturn();
await flashMessage('Saved');
}
Future<void> flashMessage(String msg) async {
message = msg;
await Future.delayed(Duration(milliseconds: 500));
message = '';
}
}The tax-return-to-edit arrives via the input property which is implemented with getters and setters.
The setter initializes the component’s own instance of the HeroTaxReturnService with the incoming return.
The getter always returns what that service says is the current state of the hero.
The component also asks the service to save and restore this tax return.
There’d be big trouble if this service were an app-wide singleton. Every component would share the same service instance. Each component would overwrite the tax return that belonged to another hero. What a mess!
Look closely at the metadata for the HeroTaxReturnComponent. Notice the providers property.
providers: [ClassProvider(HeroTaxReturnService)],The HeroTaxReturnComponent has its own provider of the HeroTaxReturnService.
Recall that every component instance has its own injector.
Providing the service at the component level ensures that every instance of the component gets its own, private instance of the service.
No tax return overwriting. No mess.
The rest of the scenario code relies on other Angular features and techniques that you can learn about elsewhere in the documentation. You can review it and download it from the live example (view source).
Scenario: specialized providers
Another reason to re-provide a service is to substitute a more specialized implementation of that service, deeper in the component tree.
Consider again the Car example from the Dependency Injection page.
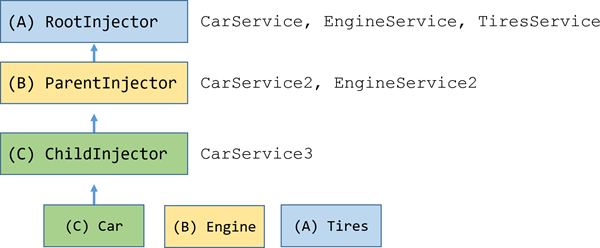
Suppose you configured the root injector (marked as A) with generic providers for
CarService, EngineService and TiresService.
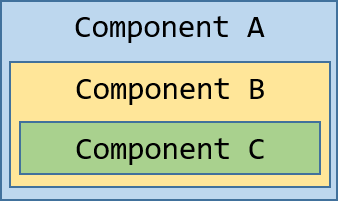
You create a car component (A) that displays a car constructed from these three generic services.
Then you create a child component (B) that defines its own, specialized providers for CarService and EngineService
that have special capabilites suitable for whatever is going on in component (B).
Component (B) is the parent of another component (C) that defines its own, even more specialized provider for CarService.
Behind the scenes, each component sets up its own injector with zero, one, or more providers defined for that component itself.
When you resolve an instance of Car at the deepest component (C),
its injector produces an instance of Car resolved by injector (C) with an Engine resolved by injector (B) and
Tires resolved by the root injector (A).
Here is the code for this cars scenario: