HTTP 6.0
In this page, you’ll make the following improvements.
- Get the hero data from a server.
- Let users add, edit, and delete hero names.
- Save the changes to the server.
You’ll teach the app to make corresponding HTTP calls to a remote server’s web API.
When you’re done with this page, the app should look like this live example (view source).
Where you left off
In the previous page, you learned to navigate between the dashboard and the fixed heroes list, editing a selected hero along the way. That’s the starting point for this page.
Before continuing with the Tour of Heroes, verify that you have the following structure.
- angular_tour_of_heroes
- lib
- app_component.{css,dart}
- src
- dashboard_component.{css,dart,html}
- hero.dart
- hero_component.{css,dart,html}
- hero_list_component.{css,dart,html}
- hero_service.dart
- mock_heroes.dart
- route_paths.dart
- routes.dart
- test
- …
- web
- index.html
- main.dart
- styles.css
- analysis_options.yaml
- pubspec.yaml
- lib
If the app isn’t running already, launch the app. As you make changes, keep it running by reloading the browser window.
Providing HTTP services
You’ll be using the Dart http package’s client classes to communicate with a server.
Pubspec updates
Update package dependencies by adding the Dart http and stream_transform packages:
Register for HTTP services
Before the app can use BrowserClient, you have to register it as a service provider.
You should be able to access BrowserClient services from anywhere in the app,
so provide it through the app’s root injector:
web/main.dart
import 'package:ngdart/angular.dart';
import 'package:ngrouter/ngrouter.dart';
import 'package:angular_tour_of_heroes/app_component.template.dart' as ng;
import 'package:http/browser_client.dart';
import 'main.template.dart' as self;
@GenerateInjector([
routerProvidersHash, // You can use routerProviders in production
ClassProvider(BrowserClient),
])
final InjectorFactory injector = self.injector$Injector;
void main() {
runApp(ng.AppComponentNgFactory, createInjector: injector);
}Notice that you supply BrowserClient as a class provider in list argument of
the generated injector. This has the same effect as the providers list in
@Component annotation.
Simulate the web API
Until you have a web server that can handle requests for hero data, the HTTP client will fetch and save data from a mock service, the in-memory web API.
Update web/main.dart with this version, which uses the mock service:
web/main.dart
import 'package:ngdart/angular.dart';
import 'package:ngrouter/ngrouter.dart';
import 'package:angular_tour_of_heroes/app_component.template.dart' as ng;
import 'package:angular_tour_of_heroes/in_memory_data_service.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart';
import 'main.template.dart' as self;
@GenerateInjector([
routerProvidersHash, // You can use routerProviders in production
ClassProvider(Client, useClass: InMemoryDataService),
// Using a real back end?
// Import 'package:http/browser_client.dart' and change the above to:
// ClassProvider(Client, useClass: BrowserClient),
])
final InjectorFactory injector = self.injector$Injector;
void main() {
runApp(ng.AppComponentNgFactory, createInjector: injector);
}Replace BrowserClient, the service that talks to the remote server,
with the in-memory web API service.
The in-memory web API service, shown below, is implemented using the
http library MockClient class.
All http client implementations share a common Client interface, so
you’ll have the app use the Client type so that you can freely switch between
implementations.
lib/in_memory_data_service.dart (init)
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:convert';
import 'dart:math';
import 'package:http/http.dart';
import 'package:http/testing.dart';
import 'src/hero.dart';
class InMemoryDataService extends MockClient {
static final _initialHeroes = [
{'id': 11, 'name': 'Mr. Nice'},
{'id': 12, 'name': 'Narco'},
{'id': 13, 'name': 'Bombasto'},
{'id': 14, 'name': 'Celeritas'},
{'id': 15, 'name': 'Magneta'},
{'id': 16, 'name': 'RubberMan'},
{'id': 17, 'name': 'Dynama'},
{'id': 18, 'name': 'Dr IQ'},
{'id': 19, 'name': 'Magma'},
{'id': 20, 'name': 'Tornado'}
];
static late List<Hero> _heroesDb;
static late int _nextId;
static Future<Response> _handler(Request request) async {
var data;
switch (request.method) {
case 'GET':
final id = int.tryParse(request.url.pathSegments.last);
if (id != null) {
data = _heroesDb
.firstWhere((hero) => hero.id == id); // throws if no match
} else {
String prefix = request.url.queryParameters['name'] ?? '';
final regExp = RegExp(prefix, caseSensitive: false);
data = _heroesDb.where((hero) => hero.name.contains(regExp)).toList();
}
break;
case 'POST':
var name = json.decode(request.body)['name'];
var newHero = Hero(_nextId++, name);
_heroesDb.add(newHero);
data = newHero;
break;
case 'PUT':
var heroChanges = Hero.fromJson(json.decode(request.body));
var targetHero = _heroesDb.firstWhere((h) => h.id == heroChanges.id);
targetHero.name = heroChanges.name;
data = targetHero;
break;
case 'DELETE':
var id = int.parse(request.url.pathSegments.last);
_heroesDb.removeWhere((hero) => hero.id == id);
// No data, so leave it as null.
break;
default:
throw 'Unimplemented HTTP method ${request.method}';
}
return Response(json.encode({'data': data}), 200,
headers: {'content-type': 'application/json'});
}
static void resetDb() {
_heroesDb = _initialHeroes.map((json) => Hero.fromJson(json)).toList();
_nextId = _heroesDb.map((hero) => hero.id).fold(0, max) + 1;
}
static String lookUpName(int id) =>
_heroesDb.firstWhere((hero) => hero.id == id, orElse: null).name;
InMemoryDataService() : super(_handler) {
resetDb();
}
}This file replaces mock_heroes.dart, which is now safe to delete.
As is common for web API services, the mock in-memory service will be
encoding and decoding heroes in JSON format, so enhance the Hero
class with these capabilities:
lib/src/hero.dart
class Hero {
final int id;
String name;
Hero(this.id, this.name);
factory Hero.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> hero) =>
Hero(_toInt(hero['id']), hero['name']);
Map toJson() => {'id': id, 'name': name};
}
int _toInt(id) => id is int ? id : int.parse(id);Heroes and HTTP
In the current HeroService implementation, a Future resolved with mock heroes is returned.
Future<List<Hero>> getAll() async => mockHeroes;This was implemented in anticipation of ultimately fetching heroes with an HTTP client, which must be an asynchronous operation.
Now convert getAll() to use HTTP.
lib/src/hero_service.dart (updated getAll and new class members)
static const _heroesUrl = 'api/heroes'; // URL to web API
final Client _http;
HeroService(this._http);
Future<List<Hero>> getAll() async {
try {
final response = await _http.get(Uri.parse(_heroesUrl));
final heroes = (_extractData(response) as List)
.map((json) => Hero.fromJson(json))
.toList();
return heroes;
} catch (e) {
throw _handleError(e);
}
}
dynamic _extractData(Response resp) => json.decode(resp.body)['data'];
Exception _handleError(dynamic e) {
print(e); // for demo purposes only
return Exception('Server error; cause: $e');
}Update the import statements as follows:
lib/src/hero_service.dart (updated imports)
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:http/http.dart';
import 'hero.dart';Refresh the browser. The hero data should successfully load from the mock server.
HTTP Future
To get the list of heroes, you first make an asynchronous call to
http.get(). Then you use the _extractData helper method to decode the
response body.
The response JSON has a single data property, which
holds the list of heroes that the caller wants.
So you grab that list and return it as the resolved Future value.
Note the shape of the data that the server returns.
This particular in-memory web API example returns an object with a data property.
Your API might return something else. Adjust the code to match your web API.
The caller is unaware that you fetched the heroes from the (mock) server. It receives a Future of heroes just as it did before.
Error Handling
At the end of getAll(), you catch server failures and pass them to an error handler.
} catch (e) {
throw _handleError(e);
}This is a critical step. You must anticipate HTTP failures, as they happen frequently for reasons beyond your control.
Exception _handleError(dynamic e) {
print(e); // for demo purposes only
return Exception('Server error; cause: $e');
}This demo service logs the error to the console; in real life, you would handle the error in code. For a demo, this works.
The code also includes an error to the caller in a propagated exception, so that the caller can display a proper error message to the user.
Get hero by id
When the HeroComponent asks the HeroService to fetch a hero,
the HeroService currently fetches all heroes and
filters for the one with the matching id.
That’s fine for a simulation, but it’s wasteful to ask a real server for all heroes when you only want one.
Most web APIs support a get-by-id request in the form api/hero/:id (such as api/hero/11).
Update the HeroService.get() method to make a get-by-id request:
lib/src/hero_service.dart (get)
Future<Hero> get(int id) async {
try {
final response = await _http.get(Uri.parse('$_heroesUrl/$id'));
return Hero.fromJson(_extractData(response));
} catch (e) {
throw _handleError(e);
}
}This request is almost the same as getAll().
The hero id in the URL identifies which hero the server should update.
Also, the data in the response is a single hero object rather than a list.
Unchanged getAll API
Although you made significant internal changes to getAll() and get(),
the public signatures didn’t change.
You still return a Future from both methods.
You won’t have to update any of the components that call them.
Now it’s time to add the ability to create and delete heroes.
Updating hero details
Try editing a hero’s name in the hero detail view. As you type, the hero name is updated in the view heading. But if you click the Back button, the changes are lost.
Updates weren’t lost before. What changed? When the app used a list of mock heroes, updates were applied directly to the hero objects within the single, app-wide, shared list. Now that you’re fetching data from a server, if you want changes to persist, you must write them back to the server.
Add the ability to save hero details
At the end of the hero detail template, add a save button with a click event
binding that invokes a new component method named save().
lib/src/hero_component.html (save)
<button (click)="save()">Save</button>Add the following save() method, which persists hero name changes using the hero service
update() method and then navigates back to the previous view.
lib/src/hero_component.dart (save)
Future<void> save() async {
await _heroService.update(hero!);
goBack();
}Add a hero service update() method
The overall structure of the update() method is similar to that of
getAll(), but it uses an HTTP put() to persist server-side changes.
lib/src/hero_service.dart (update)
static final _headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/json'};
// ···
Future<Hero> update(Hero hero) async {
try {
final url = '$_heroesUrl/${hero.id}';
final response = await _http.put(Uri.parse(url),
headers: _headers, body: json.encode(hero));
return Hero.fromJson(_extractData(response));
} catch (e) {
throw _handleError(e);
}
}To identify which hero the server should update, the hero id is encoded in
the URL. The put() body is the JSON string encoding of the hero, obtained by
calling JSON.encode. The body content type
(application/json) is identified in the request header.
Refresh the browser, change a hero name, save your change, and click the browser Back button. Changes should now persist.
Add the ability to add heroes
To add a hero, the app needs the hero’s name. You can use an input
element paired with an add button.
Insert the following into the heroes component HTML, just after the heading:
lib/src/hero_list_component.html (add)
<div>
<label>Hero name:</label> <input #heroName />
<button (click)="add(heroName)">
Add
</button>
</div>In response to a click event, call the component’s click handler and then clear the input field so that it’s ready for another name.
lib/src/hero_list_component.dart (add)
Future<void> add(InputElement event) async {
final String? name = event.value?.trim();
if (name == null || name.isEmpty) return;
heroes.add(await _heroService.create(name));
selected = null;
event.value = "";
}When the given name is non-blank, the handler delegates creation of the named hero to the hero service, and then adds the new hero to the list.
Implement the create() method in the HeroService class.
lib/src/hero_service.dart (create)
Future<Hero> create(String name) async {
try {
final response = await _http.post(Uri.parse(_heroesUrl),
headers: _headers, body: json.encode({'name': name}));
return Hero.fromJson(_extractData(response));
} catch (e) {
throw _handleError(e);
}
}Refresh the browser and create some heroes.
Add the ability to delete a hero
Each hero in the heroes view should have a delete button.
Add the following button element to the heroes component HTML, after the hero
name in the repeated <li> element.
<button class="delete"
(click)="delete(hero, $event)">x</button>The <li> element should now look like this:
lib/src/hero_list_component.html (li element)
<li *ngFor="let hero of heroes"
[class.selected]="hero == selected"
(click)="onSelect(hero)">
<span class="badge">{{hero.id}}</span>
<span>{{hero.name}}</span>
<button class="delete"
(click)="delete(hero, $event)">x</button>
</li>In addition to calling the component’s delete() method, the delete button’s
click handler code stops the propagation of the click event—you
don’t want the <li> click handler to be triggered because doing so would
select the hero that the user will delete.
The logic of the delete() handler is a bit trickier:
lib/src/hero_list_component.dart (delete)
Future<void> delete(Hero hero, Event event) async {
await _heroService.delete(hero.id);
heroes.remove(hero);
if (selected == hero) selected = null;
// This makes any component **above** <my-hero>
event.stopPropagation();
}Of course you delegate hero deletion to the hero service, but the component is still responsible for updating the display: it removes the deleted hero from the list and resets the selected hero, if necessary.
To place the delete button at the far right of the hero entry, add this CSS:
lib/src/hero_list_component.css (additions)
button.delete {
float:right;
margin-top: 2px;
margin-right: .8em;
background-color: gray !important;
color:white;
}Hero service delete() method
Add the hero service’s delete() method, which uses the delete() HTTP method to remove the hero from the server:
lib/src/hero_service.dart (delete)
Future<void> delete(int id) async {
try {
final url = '$_heroesUrl/$id';
await _http.delete(Uri.parse(url), headers: _headers);
} catch (e) {
throw _handleError(e);
}
}Refresh the browser and try the new delete functionality.
Streams
Recall that HeroService.getAll() awaits for an http.get()
response and yields a Future List<Hero>, which is fine when you are only
interested in a single result.
But requests aren’t always done only once. You may start one request, cancel it, and make a different request before the server has responded to the first request. A request-cancel-new-request sequence is difficult to implement with Futures, but easy with Streams.
Add the ability to search by name
You’re going to add a hero search feature to the Tour of Heroes. As the user types a name into a search box, you’ll make repeated HTTP requests for heroes filtered by that name.
Start by creating HeroSearchService that sends search queries to the server’s web API.
lib/src/hero_search_service.dart
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:http/http.dart';
import 'hero.dart';
class HeroSearchService {
final Client _http;
HeroSearchService(this._http);
Future<List<Hero>> search(String term) async {
try {
final response = await _http.get(Uri.parse('app/heroes/?name=$term'));
return (_extractData(response) as List)
.map((json) => Hero.fromJson(json))
.toList();
} catch (e) {
throw _handleError(e);
}
}
dynamic _extractData(Response resp) => json.decode(resp.body)['data'];
Exception _handleError(dynamic e) {
print(e); // for demo purposes only
return Exception('Server error; cause: $e');
}
}The _http.get() call in HeroSearchService is similar to the one
in the HeroService, although the URL now has a query string.
HeroSearchComponent
Create a HeroSearchComponent that calls the new HeroSearchService.
The component template is simple—just a text box and a list of matching search results.
lib/src/hero_search_component.html
<div id="search-component">
<h4>Hero Search</h4>
<input #searchBox id="search-box"
(change)="search(searchBox.value ?? '')"
(keyup)="search(searchBox.value ?? '')" />
<div>
<div *ngFor="let hero of $pipe.async(heroes)"
(click)="gotoDetail(hero)" class="search-result" >
{{hero.name}}
</div>
</div>
</div>Also, add styles for the new component.
lib/src/hero_search_component.css
.search-result {
border-bottom: 1px solid gray;
border-left: 1px solid gray;
border-right: 1px solid gray;
width:195px;
height: 20px;
padding: 5px;
background-color: white;
cursor: pointer;
}
#search-box {
width: 200px;
height: 20px;
}As the user types in the search box, a keyup event binding calls the component’s search()
method with the new search box value. If the user pastes text with mouse actions,
the change event binding is triggered.
As expected, the *ngFor repeats hero objects from the component’s heroes property.
But as you’ll soon see, the heroes property is now a Stream of hero lists, rather than just a hero list.
The *ngFor can’t do anything with a Stream until you route it through the async pipe (AsyncPipe).
The async pipe subscribes to the Stream and produces the list of heroes to *ngFor.
Create the HeroSearchComponent class and metadata.
lib/src/hero_search_component.dart
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:ngdart/angular.dart';
import 'package:ngrouter/ngrouter.dart';
import 'package:stream_transform/stream_transform.dart';
import 'route_paths.dart';
import 'hero_search_service.dart';
import 'hero.dart';
@Component(
selector: 'hero-search',
templateUrl: 'hero_search_component.html',
styleUrls: ['hero_search_component.css'],
directives: [coreDirectives],
providers: [ClassProvider(HeroSearchService)],
pipes: [commonPipes],
)
class HeroSearchComponent implements OnInit {
HeroSearchService _heroSearchService;
Router _router;
late Stream<List<Hero>> heroes;
StreamController<String> _searchTerms = StreamController<String>.broadcast();
HeroSearchComponent(this._heroSearchService, this._router) {}
void search(String term) => _searchTerms.add(term);
void ngOnInit() async {
heroes = _searchTerms.stream
.debounce(Duration(milliseconds: 300))
.distinct()
.switchMap((term) => term.isEmpty
? Stream<List<Hero>>.fromIterable([<Hero>[]])
: _heroSearchService.search(term).asStream())
.handleError((e) {
print(e); // for demo purposes only
});
}
String _heroUrl(int id) =>
RoutePaths.hero.toUrl(parameters: {idParam: '$id'});
Future<NavigationResult> gotoDetail(Hero hero) =>
_router.navigate(_heroUrl(hero.id));
}Search terms
Focus on _searchTerms:
StreamController<String> _searchTerms = StreamController<String>.broadcast();
// ···
void search(String term) => _searchTerms.add(term);A StreamController, as its name implies, is a controller for a Stream that allows you to manipulate the underlying stream by adding data to it, for example.
In the sample, the underlying stream of strings (_searchTerms.stream) represents the hero
name search patterns entered by the user. Each call to search() puts a new string into
the stream by calling add() over the controller.
Initialize the heroes property (ngOnInit)
You can turn the stream of search terms into a stream of Hero lists and assign the result to the heroes property.
late Stream<List<Hero>> heroes;
// ···
void ngOnInit() async {
heroes = _searchTerms.stream
.debounce(Duration(milliseconds: 300))
.distinct()
.switchMap((term) => term.isEmpty
? Stream<List<Hero>>.fromIterable([<Hero>[]])
: _heroSearchService.search(term).asStream())
.handleError((e) {
print(e); // for demo purposes only
});
}Passing every user keystroke directly to the HeroSearchService would create an excessive amount of HTTP requests,
taxing server resources and burning through the cellular network data plan.
Instead, you can chain Stream operators that reduce the request flow to the string Stream.
You’ll make fewer calls to the HeroSearchService and still get timely results. Here’s how:
-
transform(debounce(... 300)))waits until the flow of search terms pauses for 300 milliseconds before passing along the latest string. You’ll never make requests more frequently than 300ms. -
distinct()ensures that a request is sent only if the filter text changed. -
transform(switchMap(...))calls the search service for each search term that makes it throughdebounce()anddistinct(). It cancels and discards previous searches, returning only the latest search service stream element. -
handleError()handles errors. The simple example prints the error to the console; a real life app should do better.
Add the search component to the dashboard
Add the hero search HTML element to the bottom of the DashboardComponent template.
lib/src/dashboard_component.html
<h3>Top Heroes</h3>
<div class="grid grid-pad">
<a *ngFor="let hero of heroes" class="col-1-4"
[routerLink]="heroUrl(hero.id)">
<div class="module hero">
<h4>{{hero.name}}</h4>
</div>
</a>
</div>
<hero-search></hero-search>Finally, import HeroSearchComponent from hero_search_component.dart and add it to the directives list.
lib/src/dashboard_component.dart (search)
import 'hero_search_component.dart';
@Component(
selector: 'my-dashboard',
templateUrl: 'dashboard_component.html',
styleUrls: ['dashboard_component.css'],
directives: [coreDirectives, HeroSearchComponent, routerDirectives],
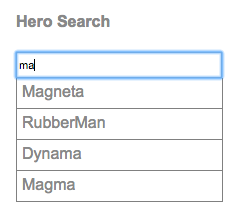
)Run the app again. In the Dashboard, enter some text in the search box. If you enter characters that match any existing hero names, you’ll see something like this.
App structure and code
Review the sample source code in the live example (view source) for this page. Verify that you have the following structure:
- angular_tour_of_heroes
- lib
- app_component.{css,dart}
- in_memory_data_service.dart (new)
- src
- dashboard_component.{css,dart,html}
- hero.dart
- hero_component.{css,dart,html}
- hero_list_component.{css,dart,html}
- hero_search_component.{css,dart,html} (new)
- hero_search_service.dart (new)
- hero_service.dart
- route_paths.dart
- routes.dart
- test
- …
- web
- main.dart
- index.html
- styles.css
- analysis_options.yaml
- pubspec.yaml
- lib
Home stretch
You’re at the end of your journey, and you’ve accomplished a lot.
- You added the necessary dependencies to use HTTP in the app.
- You refactored
HeroServiceto load heroes from a web API. - You extended
HeroServiceto supportpost(),put(), anddelete()methods. - You updated the components to allow adding, editing, and deleting of heroes.
- You configured an in-memory web API.
- You learned how to use Streams.
Here are the files you added or changed in this page.
Next step
Return to the learning path, where you can read more about the concepts and practices found in this tutorial.